HC1S80F1020AYR
- Part Number: HC1S80F1020AYR
- Categories:
- Manufacturer: Intel
- MOQ: 1PCS
- In Stock: N/A
- Datasheet:
- Description: IC FPGA 782 I/O 1020FBGA
- Payment method: Paypal/Wire transfer/Stripe/ Visa/Mastercard/AMEX
- Delivery Method: Ship within 12 hours
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount |
| Number of I/O | 782 |
| Package / Case | 1020-BBGA |
| Product Status | Obsolete |
| Total RAM Bits | 5658048 |
| Number of Gates | - |
| Voltage - Supply | 1.425V ~ 1.575V |
| Number of LABs/CLBs | 7904 |
| Operating Temperature | - |
| Supplier Device Package | 1020-FBGA (33x33) |
| Number of Logic Elements/Cells | 79040 |
HC1S80F1020AYR FPGAs Overview
HardCopy Stratix structured ASICs, Altera’s second-generation HardCopy structured ASICs, are low-cost, high-performance devices with the same architecture as the high-density Stratix FPGAs. The combination of Stratix FPGAs for prototyping and design verification, HardCopy Stratix devices for high-volume production, and the Quartus II design software beginning with version 3.0, provide a complete and powerful alternative to ASIC design and development.
HardCopy Stratix HC1S80F1020AYR devices are architecturally equivalent and have the same features as the corresponding Stratix FPGA. They offer pin-to-pin compatibility using the same package as the corresponding Stratix FPGA prototype. Designers can prototype their design to verify functionality with Stratix FPGAs before seamlessly migrating the proven design to a HardCopy Stratix structured ASIC.
The Quartus II software provides a complete set of inexpensive and easy-to-use tools for designing HardCopy Stratix devices. Using the successful and proven methodology from HardCopy APEX devices, Stratix HC1S80F1020AYR FPGA designs can be seamlessly and quickly migrated to a low-cost ASIC alternative. Designers can use the Quartus II software to design HardCopy Stratix devices to obtain an average of 50% higher performance and up to 40% lower power consumption than can be achieved in the corresponding Stratix FPGAs. The migration process is fully automated, requires minimal customer involvement, and takes approximately eight weeks to deliver fully tested HardCopy Stratix prototypes.
Features
HardCopy Stratix devices are manufactured on the same 1.5-V, 0.13 μm all-layer-copper metal fabrication process (up to eight layers of metal) as the Stratix FPGAs.
■ Preserves the functionality of a configured Stratix device
■ Pin-compatible with the Stratix counterparts
■ On average, 50% faster than their Stratix equivalents
■ On average, 40% less power consumption than their Stratix equivalents
■ 25,660 to 79,040 LEs
■ Up to 5,658,408 RAM bits available
■ TriMatrix memory architecture consisting of three RAM block sizes to implement true dual-port memory and first-in-first-out (FIFO) buffers
■ Embedded high-speed DSP blocks provide dedicated implementation of multipliers, multiply-accumulate functions, and finite impulse response (FIR) filters
■ Up to 12 PLLs (four enhanced PLLs and eight fast PLLs) per device which provide identical features as the FPGA counterparts, including spread spectrum, programmable bandwidth, clock switchover, real-time PLL reconfiguration, advanced multiplication, and phase shifting
■ Supports numerous single-ended and differential I/O standards
■ Supports high-speed networking and communications bus standards including RapidIO, UTOPIA IV, CSIX, HyperTransport technology, 10G Ethernet XSBI, SPI-4 Phase 2 (POS-PHY Level 4), and SFI-4
■ Differential on-chip termination support for LVDS
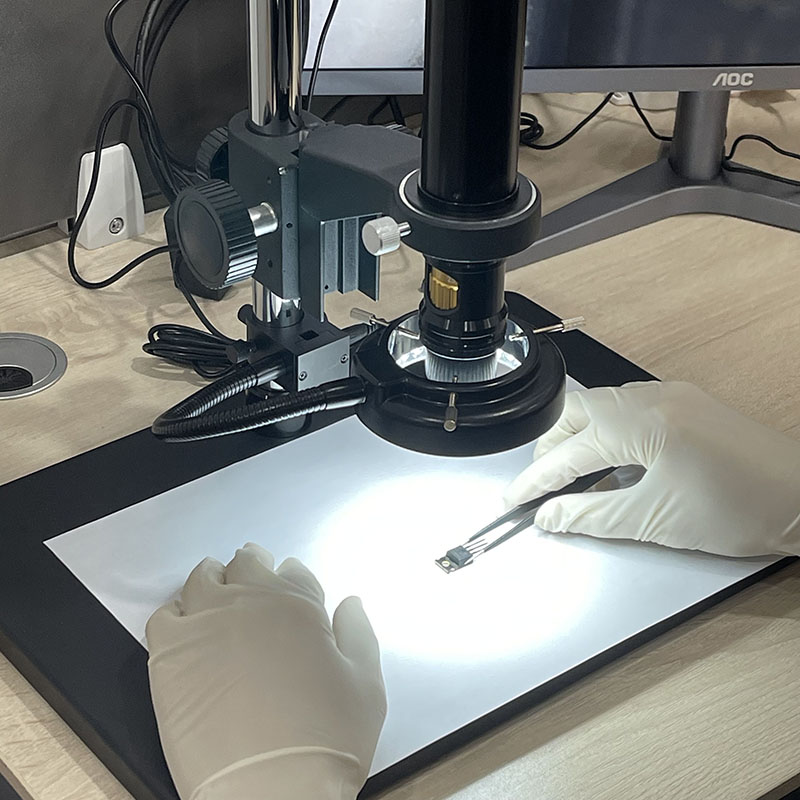 step1: Inspect Products
step1: Inspect Products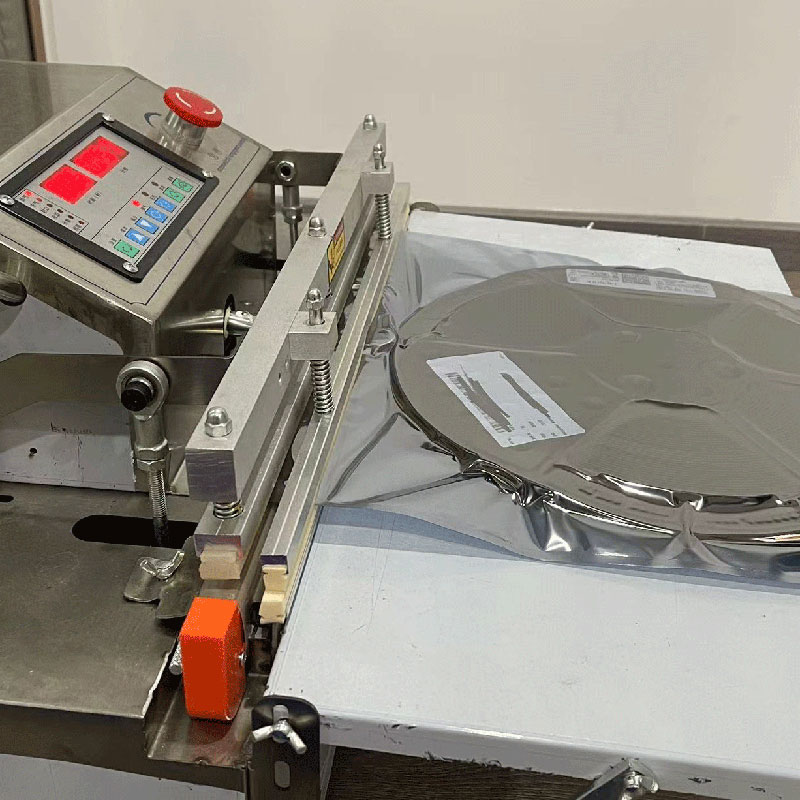 step2: Vacuum Packaging
step2: Vacuum Packaging step3: Anti-Static Bag
step3: Anti-Static Bag step4: Individual Packing
step4: Individual Packing step5: Packing Box
step5: Packing Box step6:Shipping Tag
step6:Shipping Tag

- Before shipping, we will inspect the parts to ensure it in good condition and check that the parts are brand-new and original with the datasheet. And then, all the products will be packed in an anti-static bag.
- After ensuring that there are no issues with any of the goods after packing, we will wrap them carefully and send them by international express. It demonstrates exceptional seal integrity, outstanding tear and puncture resistance, and both.

Intel Corporation, commonly known as Intel, is an American multinational technology company that specializes in the design and manufacturing of semiconductor chips and related technologies for a wide range of computing and communication devices. Intel enables designers of electronic systems to rapidly and cost effectively innovate, differentiate, and win in their markets. Intel offers FPGAs, SoCs, CPLDs, and Power Solutions, to provide high-value solutions to customers worldwide.It is one of the world's largest and most influential semiconductor chip manufacturers.
Intel's microprocessors have played a pivotal role in the development of personal computers (PCs) and other computing devices. The Intel 4004, introduced in 1971, was the world's first commercially available microprocessor. Since then, Intel has continued to innovate and release a series of successful microprocessor families, such as the Intel 8008, Intel 8086, Intel Pentium, Intel Core, and more.
- Ultra-low power consumption of STM32U575/585 microcontrollers(MCU)
- The STM32U575/585 microcontrollers (MCU) are based on the high-performance Arm 32-bit Cortex‑M33CPU with Arm TrustZone and FPU.
- TI(Texas Instruments)Advanced Ultrasonic Lens Cleaning Chipset Enables Self-Cleaning Cameras and Sensors
- Computer vision and advanced imaging have enabled many revolutionary technologies, one of the most important being Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles.
- The Best Guide to Transistor
- The transistor is electronic equipment. It is made through a p and n-type semiconductor. When a semiconductor is placed in the center between the same type of semiconductors the arrangement is called transistors.
- Electronic Component Symbols: Resistor, Capacitor, Transformers and Connectors
- Electronic components are components of electronic components and small machines and instruments. They are often composed of several parts and can be used in similar products.
- Basic Information about Temperature Sensor
- A temperature transducer is a sensor that can sense temperature and convert it into a usable output signal. The temperature sensor is the core part of the temperature measuring instrument, and there are many varieties. After entering the 21st century, temperature sensors are rapidly developing towards high-tech directions such as high precision, multi-function, bus standardization, high reliability and safety, development of virtual sensors and network sensors, and development of single-chip temperature measurement systems. The bus technology of the temperature sensor has also been standardized, and it can be used as a slave to communicate with the host through a dedicated bus interface. According to the measurement method, it can be divided into two categories: a contact type and a non-contact type. According to the characteristics of sensor materials and electronic components, it can be divided into two types: thermal resistance and thermocouple. Main Category The detection part of the contact temperature sensor is in good contact with the measured object, also known as a thermometer. The thermometer achieves heat balance through conduction or convection so that the indication value of the thermometer can directly represent the temperature of the measured object. Generally, the measurement accuracy is high. Within a certain temperature range, the thermometer can also measure the temperature distribution inside the object. However, large measurement errors will occur for moving bodies, small targets, or objects with small heat capacity. Commonly used thermometers include bimetallic thermometers, liquid-in-glass thermometers, pressure thermometers, resistance thermometers, thermistors, and thermocouples. They are widely used in industry, agriculture, commerce, and other sectors. People also often use these thermometers in daily life. With the wide application of cryogenic technology in national defense engineering, space technology, metallurgy, electronics, food, medicine, petrochemical, and other departments and the research of superconducting technology, cryogenic thermometers for measuring temperatures below 120K have been developed, such as cryogenic gas thermometers, steam Pressure thermometers, acoustic thermometers, paramagnetic salt thermometers, quantum thermometers, low-temperature thermal resistance, and low-temperature thermocouples, etc. Cryogenic thermometers require small temperature sensing elements, high accuracy, good reproducibility, and stability. The carburized glass thermal resistance made of porous high silica glass carburized and sintered is a kind of temperature sensing element of the low-temperature thermometer, which can be used to measure the temperature in the range of 1.6 ~ 300K. Its sensitive components are not in contact with the measured object, also known as a non-contact temperature measuring instrument. This instrument can be used to measure the surface temperature of moving objects, small targets, and objects with small heat capacity or rapid temperature changes (transient), and can also be used to measure the temperature distribution of the temperature field. The most commonly used non-contact thermometers are based on the fundamental law of black body radiation and are called radiation thermometers. Radiation thermometry methods include the brightness method (see optical pyrometer), radiation method (see radiation pyrometer), and colorimetric method (see colorimetric thermometer). All kinds of radiation temperature measurement methods can only measure the corresponding photometric temperature, radiation temperature, or colorimetric temperature. Only the temperature measured for a black body (an object that absorbs all radiation and does not reflect light) is the true temperature. If you want to measure the real temperature of the object, you must correct the surface emissivity of the material. However, the surface emissivity of materials depends not only on temperature and wavelength, but also on surface state, coating film, and microstructure, so it is difficult to measure accurately. In automatic production, it is often necessary to use radiation thermometry to measure or control the surface temperature of certain objects, such as the steel strip rolling temperature, roll temperature, forging temperature in metallurgy, and the temperature of various molten metals in smelting furnaces or crucibles. In these specific cases, the measurement of the emissivity of an object's surface is quite difficult. For automatic measurement and control of solid surface temperature, an additional reflector can be used to form a black body cavity together with the measured surface. The effect of additional radiation can increase the effective radiation and effective emissivity of the measured surface. Use the effective emissivity coefficient to correct the measured temperature through the instrument, and finally get the real temperature of the measured surface. The most typical additional mirror is hemispherical. The diffuse radiation on the measured surface near the center of the sphere can be reflected on the surface by the hemispherical mirror to form additional radiation, thereby increasing the effective emissivity coefficient. In the formula, ε is the surface emissivity of the material, and ρ is the reflectivity of the mirror. As for the radiation measurement of the real temperature of the gas and liquid medium, the method of inserting the heat-resistant material tube to a certain depth to form a black body cavity can be used. The effective emission coefficient of the cylinder cavity after reaching thermal equilibrium with the medium is obtained by calculation. In automatic measurement and control, this value can be used to correct the measured cavity bottom temperature (ie medium temperature) to obtain the real temperature of the medium. Advantages of non-contact temperature measurement: the upper limit of measurement is not limited by the temperature resistance of the temperature sensing element, so there is no limit to the maximum measurable temperature in principle. For high temperatures above 1800°C, non-contact temperature measurement methods are mainly used. With the development of infrared technology, radiation temperature measurement has gradually expanded from visible light to infrared and has been used below 700°C to room temperature with high resolution. Working principle Metals undergo a corresponding extension when the ambient temperature changes, so the sensor can signal this response in different ways. Bimetal Sensor A bimetal sheet is composed of two pieces of metal with different expansion coefficients attached. As the temperature changes, material A expands more than the other metal, causing the metal sheet to bend. The curvature of the bend can be converted into an output signal. Bimetal Rod and Tube Sensors As the temperature increases, the length of the metal tube (material A) increases, while the length of the non-expanding steel rod (metal B) does not increase so that the linear expansion of the metal tube can be transmitted due to the change of position. In turn, this linear expansion can be translated into an output signal. Deformation Curve Design Sensors for Liquids and Gases When the temperature changes, liquids, and gases will also produce corresponding changes in volume. Various types of structures can convert this change in expansion into a change in position, thus producing a position change output (potentiometer, sense bias, baffle, etc.). Resistance sensing As the temperature of the metal changes, its resistance value also changes. For different metals, every time the temperature changes by one degree, the resistance value changes differently, and the resistance value can be directly used as an output signal. There are two types of changes in resistance positive temperature coefficient Increased temperature = increased resistance A decrease in temperature = a decrease in resistance negative temperature coefficient Increased temperature = decreased resistance Decrease in temperature = increase in resistance Thermocouple Sensing A thermocouple consists of two metal wires of different materials welded together at the ends. Then measure the ambient temperature of the non-heating part, and the temperature of the heating point can be accurately known. Since it must have two conductors of different materials, it is called a thermocouple. Thermocouples made of different materials are used in different temperature ranges, and their sensitivities also vary. The sensitivity of the thermocouple refers to the change in the output potential difference when the temperature of the heating point changes by 1 °C. For most thermocouples supported by metallic materials, this value is between 5 and 40 microvolts/°C. Since the sensitivity of the thermocouple temperature sensor has nothing to do with the thickness of the material, it can also be made into a temperature sensor with very thin materials. Also due to the good ductility of the metal material used to make thermocouples, this tiny temperature-measuring element has a very high response speed and can measure rapidly changing processes. Selection method If you want to make reliable temperature measurements, you first need to choose the correct temperature instrument, that is, the temperature sensor. Among them, thermocouples, thermistors, platinum resistance thermometers (RTDs), and temperature ICs are the most commonly used temperature sensors in testing. The following is an introduction to the characteristics of the thermocouple and thermistor temperature instruments. thermocouple Thermocouples are the most commonly used temperature sensors in temperature measurement. Its main advantages are a wide temperature range and adaptability to various atmospheric environments, and it is strong, low in price, does not require a power supply, and is the cheapest. A thermocouple consists of two wires of dissimilar metals (metal A and metal B) connected at one end. When one end of the thermocouple is heated, there is a potential difference in the thermocouple circuit. The temperature can be calculated from the measured potential difference. However, there is a nonlinear relationship between voltage and temperature. Since the temperature is a nonlinear relationship between voltage and temperature, it is necessary to make a second measurement for the reference temperature (Tref), and use the test equipment software or hardware to process the voltage-temperature conversion inside the instrument, to Finally the thermocouple temperature (Tx), is obtained. Both Agilent34970A and 34980A data collectors have built-in measurement computing capabilities. In short, thermocouples are the simplest and most versatile temperature sensors, but thermocouples are not suitable for high-precision measurements and applications. Thermistors are made of semiconductor materials, and most of them have a negative temperature coefficient, that is, the resistance value decreases with the increase in temperature. Temperature changes will cause large resistance changes, so it is the most sensitive temperature sensor. However, the linearity of the thermistor is extremely poor and has a lot to do with the production process. Manufacturers do not give standardized thermistor curves. Thermistors are very small and respond quickly to changes in temperature. But the thermistor requires a current source, and its small size makes it extremely sensitive to self-heating errors. The thermistor measures absolute temperature on two lines and has better accuracy, but it is more expensive than a thermocouple, and its measurable temperature range is also smaller than that of a thermocouple. A commonly used thermistor has a resistance of 5kΩ at 25°C, and every 1°C temperature change causes a resistance change of 200Ω. Note that the 10Ω lead resistance causes only a negligible 0.05°C error. It is ideal for current control applications requiring fast and sensitive temperature measurements. The small size is advantageous for applications with space requirements, but care must be taken to prevent self-heating errors. Thermistors also have their measurement tricks. The advantage of the thermistor's small size is that it stabilizes quickly without causing a thermal load. However, it is also very weak, and a high current will cause self-heating. Since the thermistor is a resistive device, any current source will generate heat from power across it. Power is equal to the product of the square of the current and the resistance. So use a small current source. Permanent damage will result if the thermistor is exposed to high heat.
- Do you Know BD140 PNP Transistor: Pinout, Datasheet, Features and Applications
- The BD140 is a medium power bipolar junction PNP transistor that is mainly used for audio amplifiers and drivers utilizing complementary or quasi-complementary circuits. It is made up of silicon and comes in the TO-126 package.